Your ability to qualify for loans, credit cards, insurance coverage and eligibility to work can be seriously affected if your credit report contains errors or outdated information.
Law requires individuals to keep track of their credit report and request that inaccurate information be removed. If necessary proof of inaccurate information is presented and creditors refuse to remove the error from your credit report, you may be able to file a lawsuit and receive compensation for your losses.
Contact the experienced credit report dispute attorneys at Cory Watson Attorneys today if you need assistance in disputing inaccurate or obsolete information in your credit report. Don't wait to reach out - call our office today (877) 562-0000 or fill out our free online consultation form.
Fair Credit Reporting Act
According to the Federal Trade Commission, the Fair Credit Reporting Act promotes the accuracy, fairness, and privacy of information in the files of consumer reporting agencies.
Rights afforded to you under the FCRA include:
- Notification if the information in your file has been used against you
- Access to information in your file
- Knowledge of your credit score
- The ability to dispute inaccurate information
- Having verified inaccurate information removed from your file within 30 days of the dispute
- Ensuring outdated negative information is not reported
- The ability to limit access to your credit report
- Mandatory consent for reports provided to employers
- Removal of your name from consumer reporting agency lists for unsolicited insurance and credit offers
- The ability to seek damages from violators
Violations of the Fair Credit Reporting Act
The three primary credit reporting agencies (CRA) responsible for keeping track of consumer credit ratings in the United States are:
Errors made by these three agencies can cause significant problems for consumers. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) offers consumers protection from credit reporting agencies, banks and lenders who report inaccurate credit information, fail to fix credit report credit errors, or use a credit report for impermissible purposes.
Examples of these CRA violations include:
- Failing to report a discharged debt in bankruptcy
- Reporting information older than 7 years
- Reporting old debts as new
- Reporting a debt which was settled
- Applying late fees to debts paid on time
- Supplying credit information despite reported identity theft
- Failing to provide the debtor with the necessary information to complete the dispute process
- Mixing credit information of multiple parties
- Failing to correct inaccurate information from the debtor’s file
- Notifying all CRAs that a debtor has disputed a debt
- Failing to conduct an investigation of disputed debt within 30 days
- Failing to report results of the investigation to the debtor
- Submitting information to a CRA that is known to be incorrect
Regular review of your credit report is always a good idea in order to ensure your report is accurate.
Checking Your Credit Report
Consistently monitoring your credit is important, and could protect you from identity theft and/or fraud. Recent data breaches at Target, Uber, Home Depot and more have demonstrated how important this vigilance is. The Target breach alone compromised 110 million people's credit card information. In the last year alone, at least 14 retailers have suffered data breaches. Is your information safe?
Follow These Steps to Help Keep Yourself Protected:
- Visit annualcreditreport.com. The three credit reporting bureaus (Equifax, TransUnion, and Experian) are required by Federal Law to offer you a free copy of your credit report once per year. You will need to go one by one and request each report individually by returning to the top navigation bar after you have requested the first report to continue to the second.

- Be prepared to answer questions such as your address, height, monthly utility payment, etc. to verify your identity.
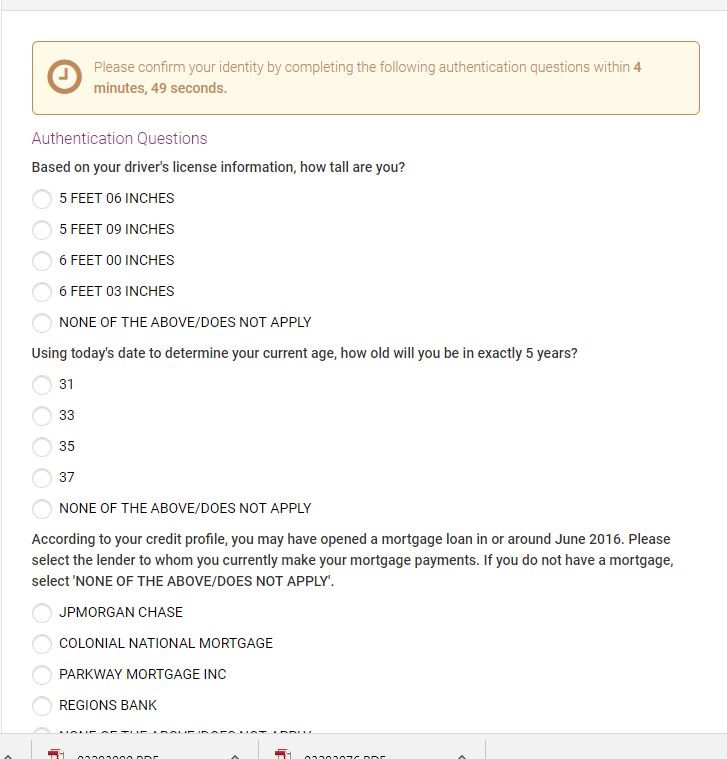
- Review your credit report to ensure there are no errors, inaccuracies, or other incorrect information. This report will not give your numerical credit score but is rather a full report of all previous activity. Negative items are usually indicated by a color other than green.
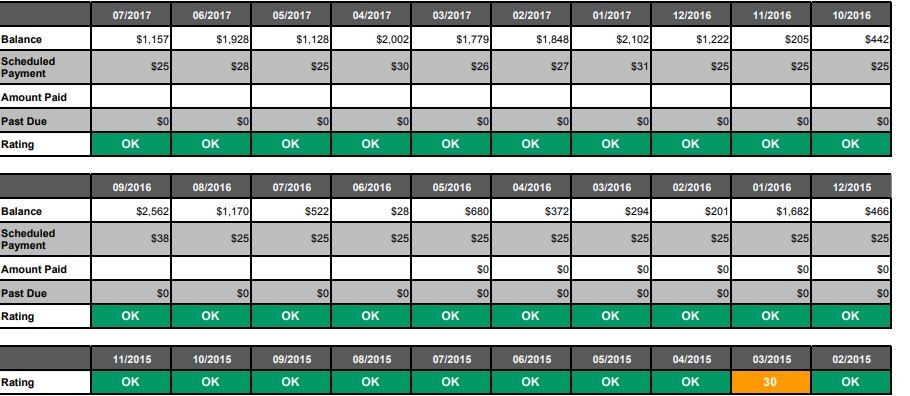
- If errors are present, you may report these inaccuracies to the agency directly through annualcreditreport.com or CreditKarma if they are with TransUnion or Equifax. These sites will allow you to dispute the claim directly on them or link you to the credit bureau where you can do it.

If you report errors on your credit report, you should receive updates from the credit reporting company. Set a reminder for 30 days and check your credit report again. If the errors that you reported have not been removed after 30 days, you may need legal representation to repair your credit.
Contact our experienced credit repair attorneys today for a FREE case evaluation - call (877) 562-000 or fill out an online case review form now.
Monitoring Your Credit Score
One way to detect whether negative reports have been made on your credit report is to monitor your credit score. To monitor your credit score, do the following:
- Sign up for CreditKarma.com, the only free service that will provide both your Transunion and Equifax numerical score and provide weekly updates.
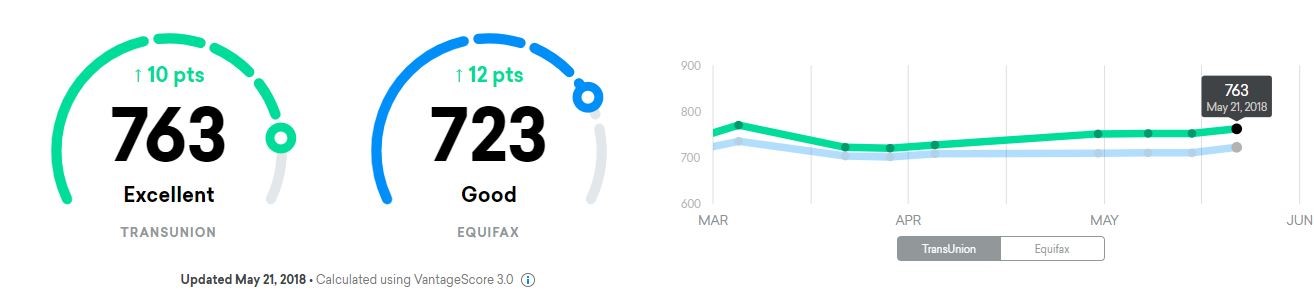
- Understand your score. There are two numerical scores that are used; a FICO score, and a VantageScore. The two scores measure the same thing (credit-worthiness), but the FICO score was introduced in 1989, whereas the VantageScore was first introduced in 2006. It is important to understand which numerical score you are looking at, and what the number means.
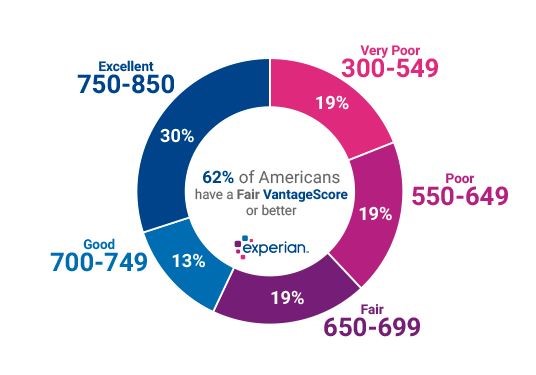
- Generally, a FICO score above 670 is considered to be "Good" and a score above 800 is considered "Exceptional."
- Generally, a Vantage Score above 700 is considered to be “Good” while above 750 is considered “Excellent."
WE ARE HERE FOR YOU 24/7
Fill out our free case review form to be contacted by an experienced credit report dispute attorney at Cory Watson Attorneys today.